Read more

The word Aschelminthes derived from Greek word (Askos; cavity and helminthes; worm) and it was first purposed by Grobben in 1910.
General Characteristics Phylum Aschelminthes;
The
members of this phylum are mostly free living, aquatic and parasitic. They are unsegmented
and bilaterally symmetrical worms. They are having slender as well vermiform body
that is generally worm like or flattened. They are generally small and microscopic
although some of them reach a meter or more in length. They are triploblastic and
pseudo-coelomate animals. Their body wall consist of syntactical and cellular
epidermis while on the outside they are covered with the thick cuticle of scleroprotein.
They are consist of longitudinal fibers. They are having straight digestive
canal with a complete mouth as well non muscular intestine and anus even though
their pharynx muscle are highly specialized. They don’t have respiratory and
circulatory systems. However their excretory system consist of protonephridia
for the mechanism of osmoregulation. They
are having simple nervous system that consists of circumenteric nerve ring along
with anterior as well posterior longitudinal nerves. They are having sense
organ in the form of Pits, Bristles Papillae and Eye spots. They are mostly dioecious
for instance, with separate sexes. The asexual reproduction is absent in them.
Their eggs consist of chit-nous shell while cleavage determinate and spiral.
Their life cycle might be simple or complicated however without any special
larval stages.
Classification of Phylum Aschelminthes;
Phylum aschelminthes are classified into the five classes.
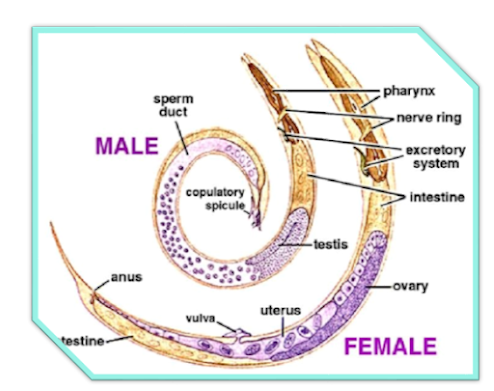
Class 1. Nematoda (Gr; nema mean
thread and eidos mean form);
The members includes in this class are
aquatic, terrestrial, free
living, parasitic, elongated in nature. They are having cylindrical, elongated
and unsegmented body. Their body wall consist of thick cuticle as well cellular, syncytial
epidermis and longitudinal muscles in four bands. The circulatory and respiratory system are absent in class nematode.
However they are having complete digestive system completes along-with muscular pharynx. Furthermore they are
having excretory system along
with glandular organs, canals or both. They are having nervous system with circumenteric ring accompanied by anterior and
posterior nerves. The member of this class are having simple sense organs. Their male member have had it penial
spicules and smaller than females.They are consist of one or two gonads. In
these animals the male genital ducts lead into the cloaca while female genital lead
to an separate opening. The phenomenon of
development in these animals are direct, however no asexual reproduction
or regeneration exist in these animals. The ascaris, necator, w
uchereria and trichinella are belong to this class. The class
nematode are differentiated into the following orders;
The
nematomorpha or Gordiacea show resemblance with nematode in general body feartures. Their Body very is long, slender, cylindrical and thin, while
their Body wall consist of thick cuticle that is bearing small papillae.They
are having single layered cellular epidermis.They are having complete digestive
system complete in the larva however it is degenerates in non feeding adults. In
nematophora the pseudocoel mostly filled with parenchyma.The circulatory, respiratory and excretory system
are absent in nematophora. However the nematophora have nervous system with a
circumenteric nerve ring as well mid-ventral nerve cord.They are having paired gonad as well gonoducts, and
their oviducts are open into the cloaca.They
are juveniles parasitic of crickets, grasshoppers and other insects. The Para-Gordius, Gordius
and Nectonema
belong to this class. The nematophora is differentiated into two orders;
Order 1; Cordioidea
Order 2; Nectonematoidea
Class 3. Rotifera(L; rota mean wheel and ferre mean to bear);
In
this class include the microscopic animals that is found in lakes, ponds, and
streams, while some of them rarely found in oceans know as wheel
bearers.Their body wall thickened into stiff plates or lorica into
which the head may lies at anterior
end with ciliated corona [wheel organ] which is used for
feeding and locomotion purpose.They are having post anal foot with toes and
adhesive glands for the purpose of attachments. They are
having musculature body with longitudinal and transverse muscle bands as well strands.Their
digestive system consist of grinding organ mastax which is
internally lined by a strong cuticle.They are being have excretory system along-with
two protonephridia as well two Protonephridial tubes, which empty into
bladders.They are having nervous system that compose of 3 major ganglia and
nerves.Their sensory organs is antennae and eyespots.In class rotifera male
smaller than females and parthenogenesis
is very common while female is oviparous without larval stages.The Asplanchna, Philodina, and Rotaria are belong to this class. This class is further divided
into three orders.
Order 1; Seisonacea
Order 2; Budelloidea
Order 3; Monogonontea
Class
4. Gastrotricha (L;gaster mean stomach and trichos mean hair);
In
this include Microscopic, marine and freshwater animals.Their body wall covered
with cuticle which bearing short, dorsal and
curved spines.In these invertebrates the corona without cilia on the
ventral surface for locomotion purpose.They are having forked posterior end
along-with adhesive tubes and glands for attachments.Their body musculature consist
of 6 pairs of longitudinal muscles.Their mouth surrounded by bristles, while their
pharynx is triradiate and muscular.They are having excretory system with
2 protonephridia. They are having saddle shape nervous system with
ganglion and 2 lateral nerves.They are exhibit by dioecious as well monoecious
and direct development take place in them. The young and adult members seems to
alike. The Macrodasys and Chaetonotus are belong to this class.
The gastrotricha is further divided into the two orders.
Order 1; Macrodasyoidea
Order 2; Chaetonotoidea
Class 5. Kinorhyncha;(Gr; kineo
mean more and rhynchos mean beak);
In
this class include marine, microscopic worm like animals. These animals exhibit superficial segmentation in
their body into 13 or 14 overlapping rings (Zonites).Their body surface compose of spiny cuticle without cilia.Their Mouth
cone or head protrusible, and covered with help of scalids. They
are being have a pair of adhesive tubes in the front part of their ventral
surface. Their Pseudocoel fluid consist of amoebocytes.They are having a nerve
ring along-with ventral cord, with a ganglion in each Zonite. Their digestive
system ends with salivary glands.These animals exhibit internal fertilization,
while metamorphosis occur with several larval stages. The Pycnophyes and Echinoderes
belong to this class. It is further divided into two orders;
Order 1; Homalorhagida
Order 2; Cyclorhagida
;;










0 Reviews